Where The Rain Falls
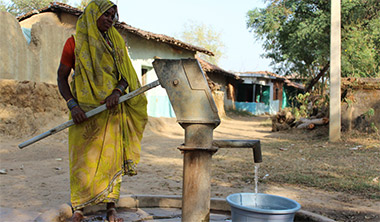
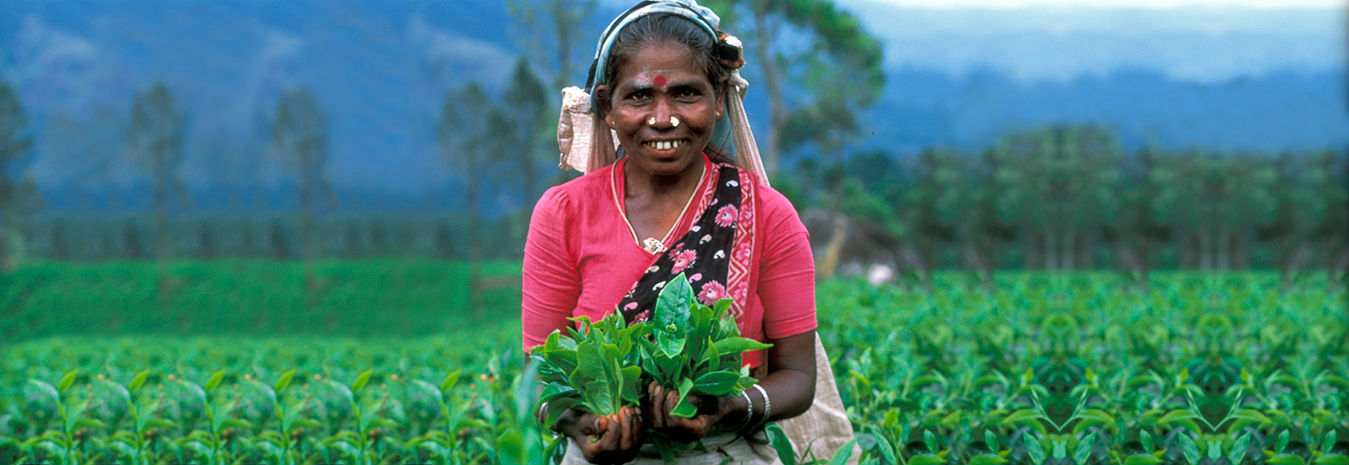
Livelihoods of India’s Adivasis and tribal communities are nearly completely dependent on natural resources. However, most of them own less than two acres of land. Adivasi communities are a historically marginalised group who are highly dependent on rain-fed agriculture (mainly paddy rice) for their livelihoods. With the changing climatic patterns, they are forced to fight climate change impacts and environmental degradation, including water stress and erratic rainfalls, soil quality and fertility deterioration, and declining agro-biodiversity.
Over the last 50 years, rainfall patterns recorded in Chhattisgarh have progressively declined by 10-15%. The Bagicha and Panthalgaon blocks are considered as drought priority areas of the Jashpur district. In addition, the forest cover has decreased sharply due to slash and burn farming, non-sustainable forest product harvesting, mining activities and urbanisation.
Consecutive crop failures, low access to safe water, low access to markets and fragile livelihoods have exacerbated food insecurity risks. To cope with the situation, people either seek external support, reduce food consumption or leave their households either for daily labour work or for several months to work in cities or mines.
Our Approach
Where the Rain Falls (WtRF) in India is a community-based in situ adaptation project to increase the resilience of Adivasi women to shocks and stresses around water, owing to climate change in Jashpur district of Chhattisgarh.
The water management approach adopted under this project for achieving water security is based on four pillars:
- Increasing water availability through on-plot and off-plot techniques
- Promoting sustainable agriculture practices
- Enabling forward looking and informed planning
- Using a rights-based and equitable approach
Water management cannot be thought in isolation. Forest, land, watershed management are to be associated to have a sustainable impact. The WTRF project has been promoting improved farming practices to ensure an optimised and sustainable use of resources to improve food security, preserve ecosystems and increase capacities to adapt to rainfalls variability.
Our Work
With the support of AXA, this project has been implemented over three phases.
Phase I of the project focused on research for situational analysis, followed by improved water management for adaptation planning. The interventions of phase II sought to address chronic risks like food and water insecurity due to climate change and how it impacts Adivasi women’s access, control, and management of natural resources. The third phase of WtRF is focussing on informing, influencing, and supporting community institutions and key development actors to adopt the CBA measures and technologies developed in the earlier phases.
The project has so far:
- Promoted strong community institutions to increase Adivasi women’s access, control, and management of resources
- Developed a cadre of community animators
- Forged linkages of Adivasi households with various government departments for various inputs, services, and entitlements
- Piloted crop improvement and diversification
- Initiated work on improved soil, land, water, and forest management with community participation in project villages
Our Innovations
Promotion of Climate Literacy
The project participants were made climate literate through modules we developed on knowledge about climate change and how to face associated challenges. Further, 18 project staff were given trained to facilitate community-level training on climate literacy. Regular hamlet-level discussions on climate change reinforce their learnings.
Micro-insurance Literacy
The insurance needs of the project participants were assessed by the project team, based on which recommendations were provided to insurance agencies on possible opportunities for offering products relevant to their risk profile. To further promote the advantages of insurance, a video was developed for generating awareness on micro-insurance and showcased among the participant households.
Community-led Soil and Water Conservation
A training module on participatory water audit and sustainable multiple-use water management has been developed for the beneficiaries, who have also been given expert guidance about soil and land development work for groundwater recharge and contingency water storage.

Our Achievements
- 01
6000
Beneficiaries have been reached through this project
- 02
1000
SHG members, farmers and VDC members from 20 project villages trained on soil and water conservation techniques
- 03
265
SHG members, farmers and Village Development Committee (VDC) members from nine villages trained on legal literacy (on legislations such as the Chhattisgarh Panchayati Raj Act and Panchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas Act (PESA))
Publications and Videos
Read about the impact of the project in these blogs:
Connect with Us
Corporate and Registered Office
Module No. 411, 4th Floor, NSIC-MDBP BuildingOkhla Industrial Estate, New Delhi – 110020 (INDIA)







