Gender Equality and Gender Transformative Change
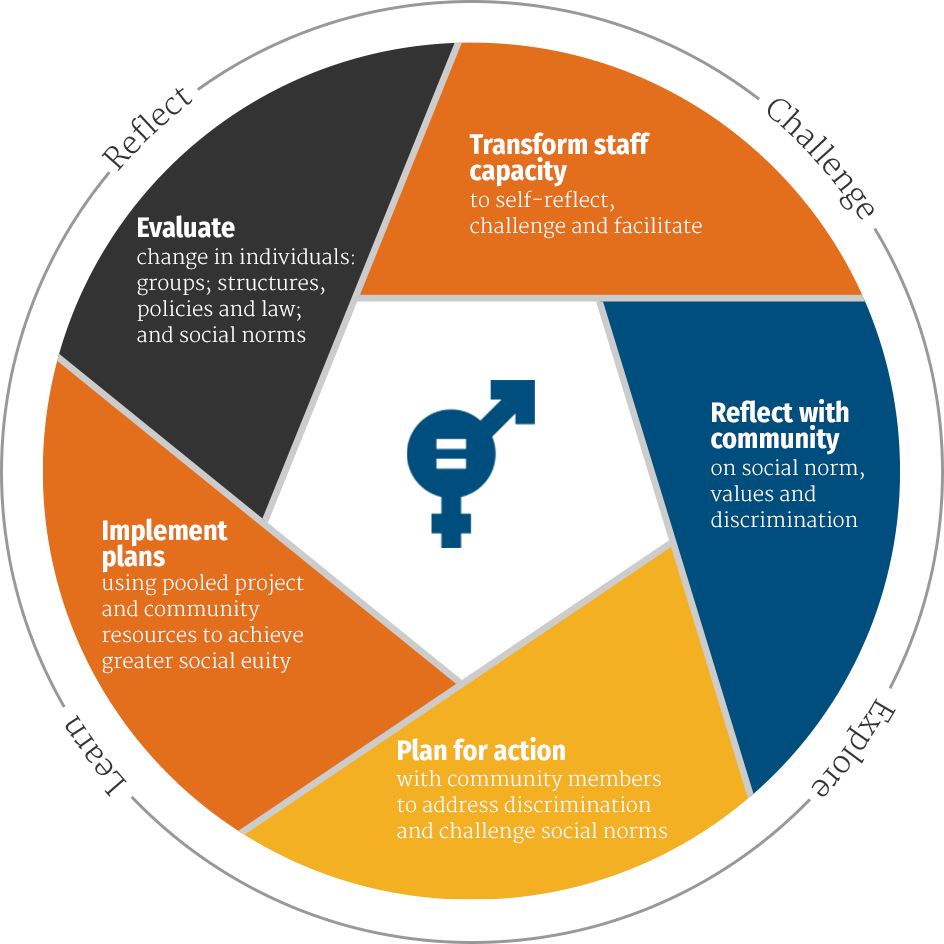
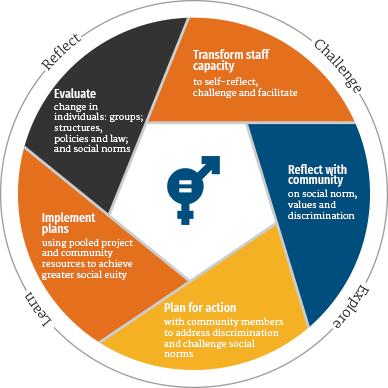
Gender equality lies at the core of all the work that CARE India does. Deep-rooted gender inequitable relations, power dynamics, and social norms in India add to the vulnerabilities and marginalisation of women in many communities. As an organization working for gender equality and women’s rights, our aim is to bring a gender transformative change at the individual, household, and community levels. Through partnerships and collaborations with local organizations, CARE India is committed to addressing gender-based violence and discrimination, promoting women’s empowerment, and advancing gender equality in all aspects of life.